
News
MoU signed for 2,400MW : China to help build four more power plants
LAHORE: A memorandum of understanding was signed between the Punjab government and a Chinese company – China Power International Holdings (CPIH) – for setting up four coal power plants of 2,400 megawatts. Energy Secretary Usman Bajwa on behalf of the Punjab government and CPIH Vice President Wang Zhiying singed the MoU. He said that the CPIH was the biggest company in the power sector of China, and under the agreement, four coal power plants would be set up in Gadani (Balochistan) and 2,400 megawatts of energy would be generated through the plants. He said that according to the agreement, two power plants would be completed within two years, while the other two within three years from the date of the agreement
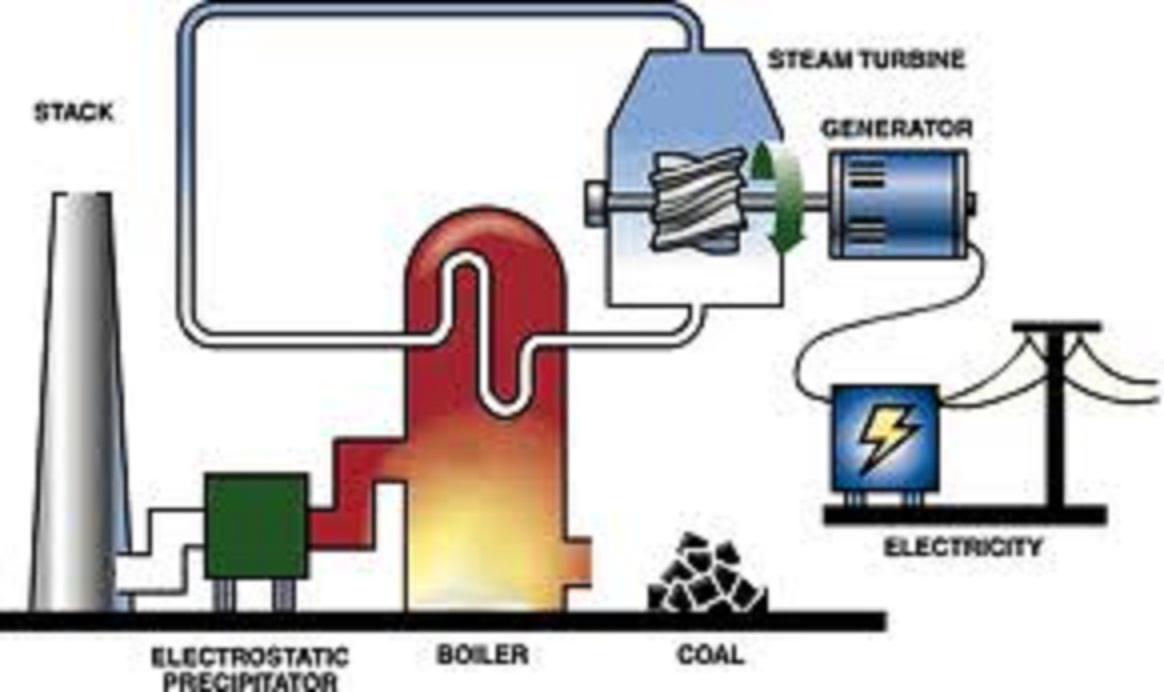
Back pressure Steam Turbine
Steam Boiler power Plant consist on Boiler + turbine +generator.
It is suitable for size 3 MW to 100 MW
These power Plants are suitable for industries who already have a steam Boiler or may arrange it. These power plants can generate Electricity at large scale. Coal , Natural Gas and furnace oil can be used as a fuel, A combination of Coal and sugar cane waste beggase can also be used to reduce the cost of fuel. Steam Turbine Power Plants are suitable for power plant size 3 MW to 100 MW
Electricity demand in Pakistan continues to grow due to chronic power shortage. Pakistan’s estimates indicate supply demand mismatch and the electricity demand is to double in the next ten years. This means that by 2015 around 15,000 MW new capacities need to be installed. Consequently more than 2,000 MW should be constructed each year just to cover the population growth.
Unfortunately most of the existing power projects planned and proposed today in Pakistan continue to focus heavily on imported oil. Oil based power plants are expensive, damaging to environment and also continues to increase Pakistan’s foreign deficit. Fortunately, government of Pakistan has recognized Biomass to be a important renewable resource and has created an attractive Alternative Renewable Energy (ARE) policy that offers many incentives to investors to utilize this local and green resource. Pakistan ranks No. 6 in the world in Sugar can production. Sugar Mills in Punjab can produce Electricity from sugar cane Waste Bagasse. with high pressure Boilers and back pressure steam turbines |
|
SUGAR GROUP is working on multiple sites in Pakistan that is capable of supporting 10 to 20 MW of biomass power plant, capable of utilizing different kind of biomass fuel. By using Biomass SUGAR GROUP plans will not just offer electricity but will also help in disposal of biomass residues, use abundant indigenous resources, help power remote locations that are rich in biomass resources and offer a clean renewable energy option. By 2015, SUGAR GROUP plans to build 5 small biomass projects in Pakistan.
The first SUGAR GROUP biomass project is a 10 MW power plant on Build Operate Own (BOO) terms. The Project will be using biomass, such as baggase, cane trash and rice husk as a fuel sources. The project would comprise of a boiler and steam turbine/generator (with gross capacity of 12MW) along with related accessories.
The proposed power plant is based on steam turbine generator consisting of a single boiler and a single steam turbine/generator. The selected technology is considered to be very effective yet economical as the fuel biomass/coal is abundantly available domestically at a reasonable price. During off or drought seasons, the power plant will be able to us coal as an alternate fuel. | |
Punjab can produce 5,000MW from biomass: report
Punjab has the potential to produce 3,000-5,000 MW of electricity from biomass the province generates annually as agricultural waste states a report “Identification of Biomass Potential in Punjab,” prepared by German NGO GIZ.
Most of the 35 million ton biomass generated annually in Punjab goes waste through inefficient burning, the report said.
The main contributors to biomass are bagasse, rice straw and husk, cotton waste, barley residue, maize stalks and leaves, and millet and sorghum stalks.
Sugarcane provides two major crop wastes; barbojo – the leaves and stalks of the cane and bagasse – the dry pulpy residue left after the extraction of juice from sugarcane. The cotton crop also gives significant residue in the form of stalks and husks.
“We carried out detailed survey of all the36 districts of the province to find out the amount of biomass that is available,” said Amir of GIZ who was member of the team that prepared the report after painstaking research. He said the currently available power potential by using biomass as fuel is around 3,000 MW. This could increase to 5,000 MW if the sugar mills consume 97 percent of the available bagasse in highly efficient boilers.
Sugar mills produce around 30-32 million tons of bagasse each year during the sugar cane crushing season. The mills sell only 30,000 tons of bagasse in the market and consume the rest for power generation,
Total production of each crop contributing to biomass was calculated in each district of Punjab and the biomass residue generated from the crop was also evaluated. The findings showed that the energy deficient province has enough potential of generating electricity trough biomass.
Most of the sugar mills consume bagasse in heating inefficient boilers of 12 to 20 bar. The Indian sugar mills have installed 50 bar or above boilers that produce many times more electricity, he said.
Punjab could produce 203 MW of electricity from 30,000 ton bagasse provided to the market which could increase manifold with increase in supply of bagasse that could be spared if mills use high bar efficient boilers, Butt said.
According to the report rice husk that contains 10.4 percent moisture content and 64.25 percent volatile matter has caloric value of 3,826 kacl/kg. Moisture content in cotton stalk is 20.86 percent, volatile matter 60.66 percent, and it has gross calorific value of 3,296 kcal/kg. Wheat straw has calorific value of 3,712 kacl/kg with only 6.34 percent water content and 61.73 percent volatile matter. Bagasse contains 25.25 percent moisture, 48.98 percent volatile matter and its caloric value is 3,673 kcal/kg.
Report points out that the efficient use of biomass as fuel would reduce carbon print in the environment. Currently, most of these biomass products are treated as biomass waste and usually burned in the fields. Biomass burning has a significant impact on global atmosphere chemistry since it provides large sources of carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides and hydrocarbons.
K.S. Amir
3-A Davis Road, Lahore 54000 Pakistan
E.Mail : powerplants786@gmail.com







I love this article. Even though, it was written some time ago it is very relevant for what I am doing right now. My question to the author is how many megawatts is required a country of say 5 million with a major city of 2 million with very little industrial consumption but mostly rural and domestic usage.
ReplyDelete